Electrochemical energy storage includes lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, sodium-sulfur batteries, and flow batteries.
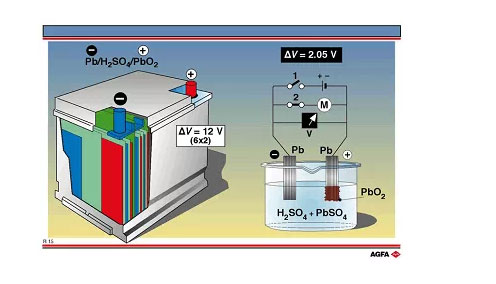
(1) Lead-acid battery: It is a battery whose electrode is mainly made of lead and its oxide, and the electrolyte is a sulfuric acid solution. It is widely used in the world, with a cycle life of about 1000 times, efficiency of 80%-90%, and high cost performance. It is often used in accident power or backup power of power systems.
Inadequacies: If the depth, fast and high power discharge, the available capacity will drop. It is characterized by low energy density and short life. Lead-acid batteries have increased their cycle life by adding super-active carbon materials to the negative plates of lead-acid batteries this year.
(2) Lithium-ion battery: It is a type of battery that uses a lithium metal or a lithium alloy as a negative electrode material and uses a non-aqueous electrolyte solution. Mainly used in portable mobile devices, its efficiency can reach more than 95%, the discharge time can reach several hours, the number of cycles can reach 5000 times or more, and the response is fast. It is the most energy-efficient battery in the battery. Use the most. In recent years, technology has been continuously upgraded, and positive and negative materials have many applications.
The mainstream power lithium batteries in the market are divided into three categories: lithium cobalt oxide batteries, lithium manganese oxide batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries. The former has a high energy density, but the safety is slightly worse. On the contrary, domestic electric vehicles such as BYD currently use lithium iron phosphate batteries. But it seems that foreigners are playing ternary lithium batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries?
The lithium-sulfur battery is also very hot. It is a kind of battery with sulfur as the positive electrode and metallic lithium as the negative electrode. The theoretical specific energy density can reach 2600 wh/kg, and the actual energy density can reach 450 wh/kg. However, how to greatly increase the charge and discharge cycle life and safety of the battery is also a big problem.
Inadequacies: There are safety issues such as high price (4 yuan / wh), overcharge leading to heat, burning, etc., need to be charged.
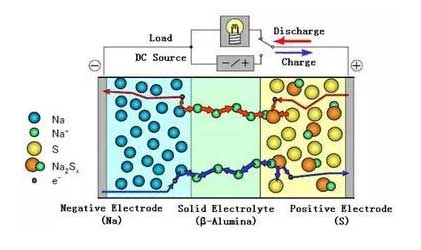
(3) Sodium-sulfur battery: It is a secondary battery using metal sodium as a negative electrode, sulfur as a positive electrode, and a ceramic tube as an electrolyte separator. The cycle can reach 4500 cycles, the discharge time is 6-7 hours, the cycle round-trip efficiency is 75%, the energy density is high, and the response time is fast. At present, more than 200 such energy storage power stations have been built in Japan, Germany, France, and the United States, mainly for load leveling, peak shifting and improved power quality.
Inadequacies: Because of the use of liquid sodium, it runs at high temperatures and is easy to burn. And if the grid is out of power, diesel generators are needed to help maintain high temperatures, or to help meet the conditions for battery cooling.
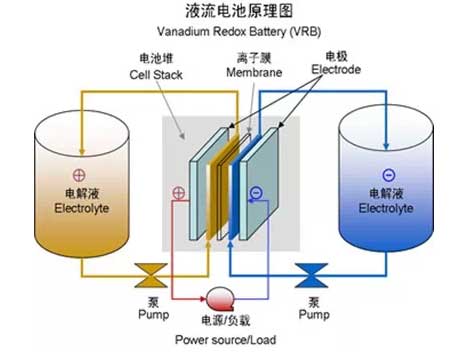
(4) Flow battery: A high-performance battery that is separated by a positive and negative electrode electrolyte and circulated separately. The power and energy of the battery are irrelevant. The energy stored depends on the size of the storage tank, so it can store energy for hours to days, up to MW. This battery has multiple systems, such as iron-chromium system, zinc-bromine system, sodium polysulfide bromine system and all-vanadium system, of which vanadium batteries are the hottest.
Inadequacies: The battery is too large; the battery is too high for the ambient temperature; the price is expensive (this may be a short-term phenomenon); the system is complicated (it is the pump and the pipeline, which is not like the non-flow battery such as lithium battery So simple).
Battery storage has more or less environmental problems.




