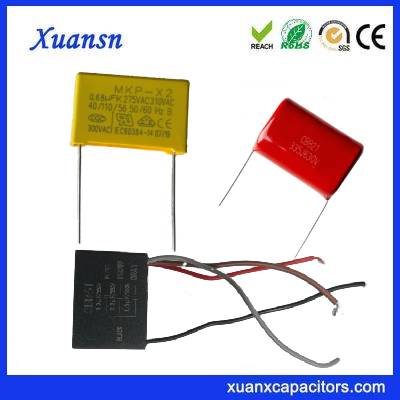
- Metallized Polypropylene Film
- MKP Capacitor
- High Insulation Resistance
- Low Dielectric Absorption
- XUANSN Manufacturer
MKP Capacitor CBB21 X2 Metallized Polypropylene Film XUANSN Manufacturer
Description
MKP capacitor Overview:
The MKP capacitor, also known as the metallized polypropylene capacitor, is a high-quality electronic component widely used in various industries and applications. With its exceptional performance and reliability, the MKP capacitor is designed to meet the demanding requirements of modern electronic systems.
MKP capacitor Definition:
The MKP capacitor is a type of film capacitor that utilizes a metallized polypropylene film as the dielectric material. It is known for its excellent electrical properties, including high insulation resistance, low dielectric absorption, and low dissipation factor. The capacitor is designed to store and discharge electrical energy efficiently, making it an essential component in many electronic circuits.
Structure:
The MKP capacitor features a robust and compact structure. It consists of two metal electrodes that are sandwiched between a polypropylene film. The metal electrodes are typically made of aluminum or zinc-aluminum alloy, and they are metallized to provide a uniform conducting surface. The metallized electrodes ensure a stable and reliable electrical connection, while the polypropylene film acts as the dielectric material, providing excellent insulation and energy storage capabilities.
Characteristics:
- High Insulation Resistance: The MKP capacitor offers high insulation resistance, preventing leakage of electrical current and ensuring reliable operation.
- Low Dielectric Absorption: It exhibits low dielectric absorption, enabling quick charging and discharging cycles.
- Low Dissipation Factor: The capacitor has a low dissipation factor, minimizing energy losses during operation and maintaining high efficiency.
- Excellent Temperature Stability: It maintains stable electrical characteristics over a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various environments.
- Self-healing Properties: In case of minor dielectric breakdown, the MKP capacitor has the ability to repair itself, ensuring prolonged operational life.
Applications:
The MKP capacitor finds applications across a broad range of industries and electronic systems, including but not limited to:
- Power Electronics: Used in power supplies, inverters, motor drives, and renewable energy systems for energy storage, filtering, and power factor correction.
- Audio and Video Equipment: Employed in audio amplifiers, speakers, televisions, and multimedia systems to ensure high-quality signal processing and filtering.
- Lighting Systems: Used in ballasts, LED drivers, and fluorescent lamps to improve power efficiency and stabilize voltage.
- Industrial Automation: Applied in control circuits, robotics, and PLCs to enhance operational efficiency and reliability.
- Automotive Electronics: Utilized in automotive ignition systems, electric vehicle charging, and onboard power management for improved performance and safety.
Which of the common capacitors are MKP materials?
MKP capacitors can be divided into different types based on their specific characteristics and intended applications. Here are some common types of MKP capacitors:
- General-Purpose MKP Capacitors: These capacitors are designed for general electronic applications and offer a balance between performance and cost. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including power supplies, audio/video equipment, lighting systems, and industrial automation.
- High Voltage MKP Capacitors: These capacitors are specifically designed to withstand higher voltage levels. They are used in applications such as power distribution systems, high-voltage power supplies, and electric vehicle charging stations, where voltage requirements exceed those of general-purpose capacitors.
- Pulse MKP Capacitors: Pulse MKP capacitors are designed to handle high-energy pulses and fast switching applications. They have low inductance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), making them suitable for power electronics, motor drives, and high-frequency circuits.
- Snubber MKP Capacitors: Snubber capacitors are used in power electronics circuits to suppress voltage spikes and transient overvoltages. They are designed to handle high peak currents and high voltage stress. Snubber capacitors find applications in motor drives, inverters, and switching power supplies.

- X2/Y2 Safety MKP Capacitors: X2 and Y2 safety capacitors are specifically designed for applications requiring enhanced safety measures, such as electrical and electronic equipment connected to mains power. X2 capacitors are used across the line (L-N) to suppress common-mode interference, while Y2 capacitors are used between the line and ground (L-G) for differential-mode filtering.

- Miniature MKP Capacitors: Miniature MKP capacitors are compact in size and are designed for space-constrained applications. They are commonly used in small electronic devices, PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards), and portable electronics.
- Motor Run MKP Capacitors: Motor run capacitors are designed for use in electric motors to improve their starting torque, power factor correction, and motor efficiency. These capacitors can handle continuous high-current operation and are built to withstand harsh conditions.
-300x300.png)
It’s important to note that different manufacturers may have their own designations and naming conventions for these capacitor types, but the general categorization remains consistent across the industry. When selecting an MKP capacitor, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your application and choose the appropriate type that best suits your needs.
What is the main difference between MKP material and MKT?
The main difference between MKP (Metallized Polypropylene) material and MKT (Metallized Polyester) material lies in the dielectric materials used in each case. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
- Dielectric Material: MKP capacitors use a polypropylene film as the dielectric material, while MKT capacitors use a polyester (also known as PET) film as the dielectric material. The choice of dielectric material impacts the electrical properties and performance of the capacitor.
- Temperature Stability: MKP capacitors typically offer better temperature stability compared to MKT capacitors. Polypropylene has a higher melting point and better thermal resistance, allowing MKP capacitors to maintain stable electrical characteristics over a wider temperature range. MKT capacitors, on the other hand, may experience a slight shift in capacitance and other electrical parameters with temperature variations.
- Dielectric Absorption: MKP capacitors generally exhibit lower dielectric absorption than MKT capacitors. Dielectric absorption refers to the tendency of a capacitor to retain a charge temporarily after being discharged. MKP capacitors have low dielectric absorption, which makes them suitable for applications that require rapid charging and discharging cycles.
- Dissipation Factor: MKP capacitors tend to have a lower dissipation factor (DF) compared to MKT capacitors. The dissipation factor is a measure of energy losses in the capacitor due to internal resistance and dielectric losses. A lower dissipation factor indicates higher efficiency and reduced energy losses in the capacitor.
- Application Focus: MKP capacitors are often preferred in applications that require high performance, such as power electronics, audio/video equipment, and industrial automation. Their excellent electrical properties, temperature stability, and low dielectric absorption make them suitable for demanding applications. MKT capacitors are commonly used in general-purpose applications, consumer electronics, and less demanding circuits where cost-effective solutions are desired.
It’s important to note that the choice between MKP and MKT capacitors depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as temperature range, dielectric absorption, dissipation factor, and cost considerations need to be taken into account when selecting the appropriate capacitor type for a particular application.
Conclusion:
The MKP capacitor stands as a reliable and versatile component, offering superior electrical characteristics and outstanding performance. Its high insulation resistance, low dielectric absorption, and low dissipation factor make it a preferred choice for various applications in diverse industries. Whether in power electronics, audio systems, lighting, industrial automation, or automotive electronics, the MKP capacitor plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability in electronic circuits. Choose the MKP capacitor for your electronic projects and experience the benefits of its exceptional design and functionality.





