Identifying polar capacitors can be done through visual inspection and by referring to markings on the capacitor itself. Here are some steps to help you identify polar capacitors:
- Look for markings: Polar capacitors typically have markings on them that indicate their polarity. The positive terminal is usually marked with a “+” symbol, while the negative terminal may be marked with a “-” symbol or a solid line. These markings can be found directly on the body of the capacitor or on the capacitor’s label.
- Check for color-coding: In some cases, polar capacitors may have color-coded markings to indicate polarity. The positive terminal may be color-coded with a specific color or a band, while the negative terminal may have a different color or no color band.
- Observe the physical design: Polar capacitors often have a specific physical design that can help in identifying their polarity. The negative terminal may have a shorter lead or a flat edge on the capacitor body, while the positive terminal may have a longer lead or a rounded edge.
- Refer to datasheets or documentation: If the markings on the capacitor are unclear or absent, you can refer to the capacitor’s datasheet or the manufacturer’s documentation. These resources typically provide detailed information about the capacitor, including its polarity and terminal identification.
It’s important to note that not all capacitors are polarized. Non-polarized capacitors, such as ceramic capacitors, film capacitors, or tantalum capacitors, do not have specific polarity and can be connected in either direction. However, for electrolytic capacitors and some other specialized capacitors, it is crucial to correctly identify the polarity and connect the positive and negative terminals accordingly to ensure proper functionality and prevent damage.
For example,the circuit uses different capacitor according to different functions. Simple-function circuits mostly use polystyrene non-polar capacitor, while multi-function circuits use not only polystyrene non-polar capacitor, but also use porcelain, polyester (polyester), and paper. Non-polar capacitor such as dielectrics, mica, and other polar capacitor such as aluminum electrolytic capacitor and tantalum electrolytic capacitor, among which tantalum capacitors have higher stability.
The main function of the capacitor in the circuit is filtering, coupling, delay and so on. It is represented by the letter “C” in the circuit, and the electrolytic capacitor is represented by “E” in some circuits. The names, characteristics, circuit symbols, and physical appearance of common capacitors are shown in Table 1-1.
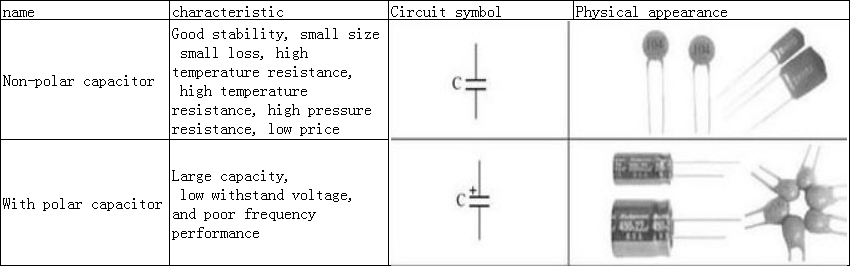
Table 1-1 Names, characteristics, circuit symbols, physical shapes of common capacitors