What is the bypass capacitor?
A capacitor that bypasses the high-frequency component of an AC signal mixed with a high-frequency current and a low-frequency current is referred to as a “bypass capacitor.”
The main function of the bypass capacitor is to create an AC shunt that eliminates unwanted energy entering the susceptible region, ie when mixed with high frequency and low frequency signals are amplified by the amplifier, only a certain level is allowed to pass. When the low frequency signal is input to the next stage without high frequency signal input, add an appropriate size grounding capacitor at the input of the stage so that the higher frequency signal is easily bypassed by this capacitor (this is because The capacitor has a small impedance to the high frequency, and the low frequency signal is sent to the next stage for amplification due to the large impedance of the capacitor.
For the same circuit, the bypass capacitor is used to filter the high-frequency noise in the input signal, filtering the high-frequency noise carried by the pre-stage, and decoupling (also called decoupling). Capacitance is the filtering of the output signal as a filtering object.
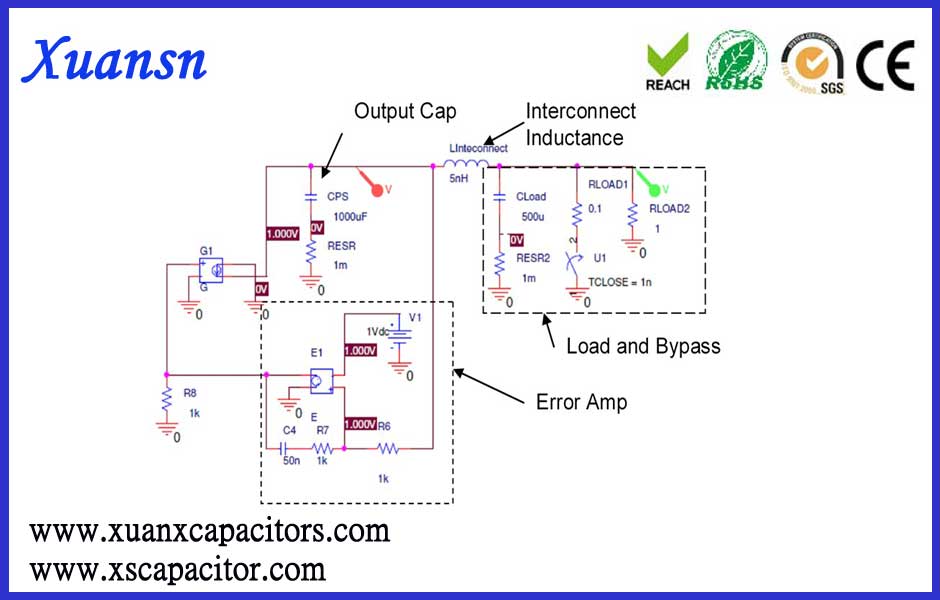
Bypass capacitor related comparison
Bypass capacitors are not a theoretical concept, but a practical method that is often used. Tubes or transistors need to be biased to determine the DC supply conditions at the operating point. For example, the gate of the electron tube is required to be negatively charged with respect to the cathode. In order to operate under a direct current power source, a resistor is connected in series from the cathode to the ground, and a positive potential of the cathode is formed by the plate current, and the gate is grounded. This biasing technique is called “self-biasing”, but for (AC) signals, this is also a negative feedback. To eliminate this effect, a large enough capacitor is connected in parallel with this resistor. This is called bypass. capacitance.