The working principle of capacitors is to store electrical energy by storing charges on the electrodes, usually used together with inductors to form an LC oscillation circuit. The working principle of capacitors is that the charge will move under the force of the electric field. When there is a medium between the conductors, it will hinder the movement of the charge and cause the charge to accumulate on the conductor, resulting in the accumulation of charge.
Capacitors are one of the electronic components used in a large number of electronic equipment, so they are widely used in DC blocking, coupling, bypass, filtering, tuning loop, energy conversion, control circuit, etc.
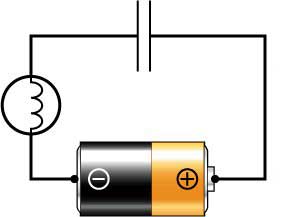
A capacitor is similar to a battery and has two electrodes. Inside the capacitor, these two electrodes are connected to two metal plates separated by a dielectric. The dielectric can be air, paper, plastic, or any other material that does not conduct electricity and prevents the two metal poles from coming into contact with each other.
The metal plate on the capacitor connected to the negative electrode of the battery will absorb the electrons generated by the battery. The metal plate on the capacitor connected to the positive electrode of the battery will release electrons to the battery. After charging, the capacitor and the battery have the same voltage (if the battery voltage is 1.5 volts, the capacitor voltage is also 1.5 volts).
If you are interested in electrolytic capacitor you could click it.